Preparation of Guar Gum Solutions
Guar Gum (E412) is a readily soluble in cold water, forming a high viscosity solution at low concentrations which increases in viscosity as temperature rises. It is widely used for its gelling, thickening and stabilizing effect on emulsions and suspensions and often blended with other rheology modifiers, particularly Xanthan gum as the two combine to give greatly increased effects.
The Process
Gum solutions may be prepared along with the other ingredients in the batch or separately, sometimes in concentrated form. Processing methods vary widely according to the scale of manufacture, ingredients and viscosity of the end product, but basic requirements are the same. These include:
- Where the gum is added along with other ingredients in the batch, it is usually preferable to disperse and hydrate the gum first to avoid reactions with other ingredients such as salt or acids like vinegar; the presence of these in the formulation can slow the hydration rate dramatically.
- Guar gum (like other rheology modifiers) has a strong tendency to form lumps when added to the water. To reduce this risk it may be premixed with other powdered ingredients such as sugar (which will not effect hydration rate) this acts as a dispersion aid to reduce the formation of agglomerates by separating the particles.
- Similarly the gum may be dispersed into non-aqueous phase liquids such as oils, alcohols or glycols. This “slurry” is then added to the aqueous phase allowing the gum to hydrate with a reduced risk of lump formation.
- Where separate or concentrated gum solutions are prepared dispersion aids are obviously not an option. The powder has to be added to the liquid under vigorous agitation at a controlled rate to reduce the formation of agglomerates.
- With readily soluble gums such as guar the powder must also be added rapidly because addition of powder becomes increasingly difficult as the viscosity increases.
Case Study: Gum Solution Made 40x Faster with High Shear Mixing
The Problem
Dispersion of gums and thickeners using conventional agitators can give rise to several problems:
- Even when the above steps are taken agglomerates can easily form. This can be exacerbated by operator error. Agitators do not produce sufficient shear to rapidly break these down, leading to long mixing times and low yield. Many formulations contain unnecessarily high levels of gum to compensate for this, increasing raw material costs.
- Premixing powders or non-aqueous phase liquid with the gum addes to process time and costs.
- Unhydrated gum can gradually hydrate during storage or subsequent processing, leading to undesired changes in product viscosity and stability.
- It is not possible to create high percentage gum solutions with traditional methods. Solutions of this type may be required in certain applications where water is limited in the formulation.
The Solution
A Silverson High Shear mixer can produce an agglomerate-free dispersion and fully hydrate Guar gum in a fraction of the time taken by conventional methods.
These advantages stem from the three stage mixing/shearing action of the Silverson rotor/stator mixer. This operates as follows:

Stage 1
The vessel is charged with liquid and the mixer is started. The gum is added to the water as rapidly as possible. The high speed rotation of the rotor blades creates a powerful suction which draws the liquid and powder into the workhead where they are rapidly mixed.

Stage 2
Centrifugal force drives the powder and liquid towards the periphery of the workhead, where they are subjected to intense high shear in the gap between the rotor and stator wall. The product is forced out of the stator and projected radially back into the body of the mix.
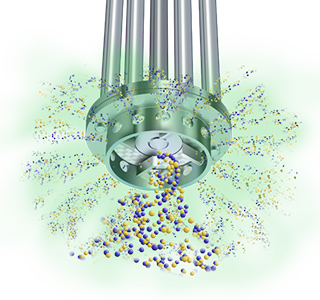
Stage 3
Fresh materials are simultaneously drawn into the workhead. In a short mixing cycle all the material passes many times through the workhead, progressively reducing the particle size and exposing an increasing surface area to the surrounding liquid, accelerating hydration.
-
Stage 1

Stage 1
The vessel is charged with liquid and the mixer is started. The gum is added to the water as rapidly as possible. The high speed rotation of the rotor blades creates a powerful suction which draws the liquid and powder into the workhead where they are rapidly mixed.
-
Stage 2

Stage 2
Centrifugal force drives the powder and liquid towards the periphery of the workhead, where they are subjected to intense high shear in the gap between the rotor and stator wall. The product is forced out of the stator and projected radially back into the body of the mix.
-
Stage 3

Stage 3
Fresh materials are simultaneously drawn into the workhead. In a short mixing cycle all the material passes many times through the workhead, progressively reducing the particle size and exposing an increasing surface area to the surrounding liquid, accelerating hydration.
The Advantages
- Maximized yield/functionality allows products to be formulated with reduced gum content, cutting raw material costs.
- Agglomerate-free mix.
- Operator error is effectively eliminated.
- Rapid mixing times.
- Consistent product quality and repeatability.
- Premixing of gum with powders or non-aqueous phase is not required.
The batch size, formulation, type of ingredients and the viscosity of the end product dictates which Silverson model is best suited to processing requirements:
Silverson Ultramix
- Excellent in-tank movement
- Capable of rapidly incorporating large volumes of powders
- Ultra Sanitary CIP design
- Ideal for higher viscosity mixes
- Low maintenance
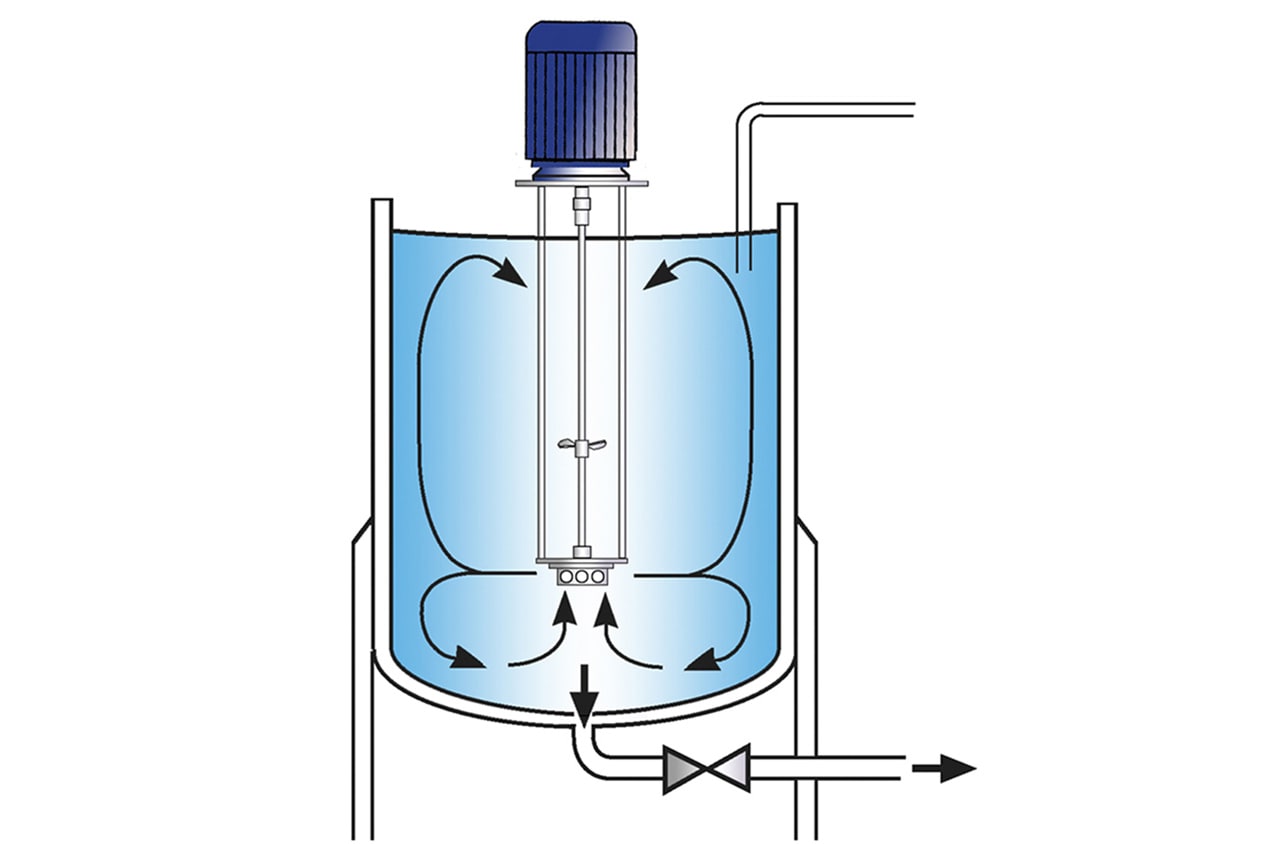
High Shear Batch Mixers
- Suitable for batches up to 400 US gallons
- Can be used on mobile floor stands
- Can easily be moved from vessel to vessel
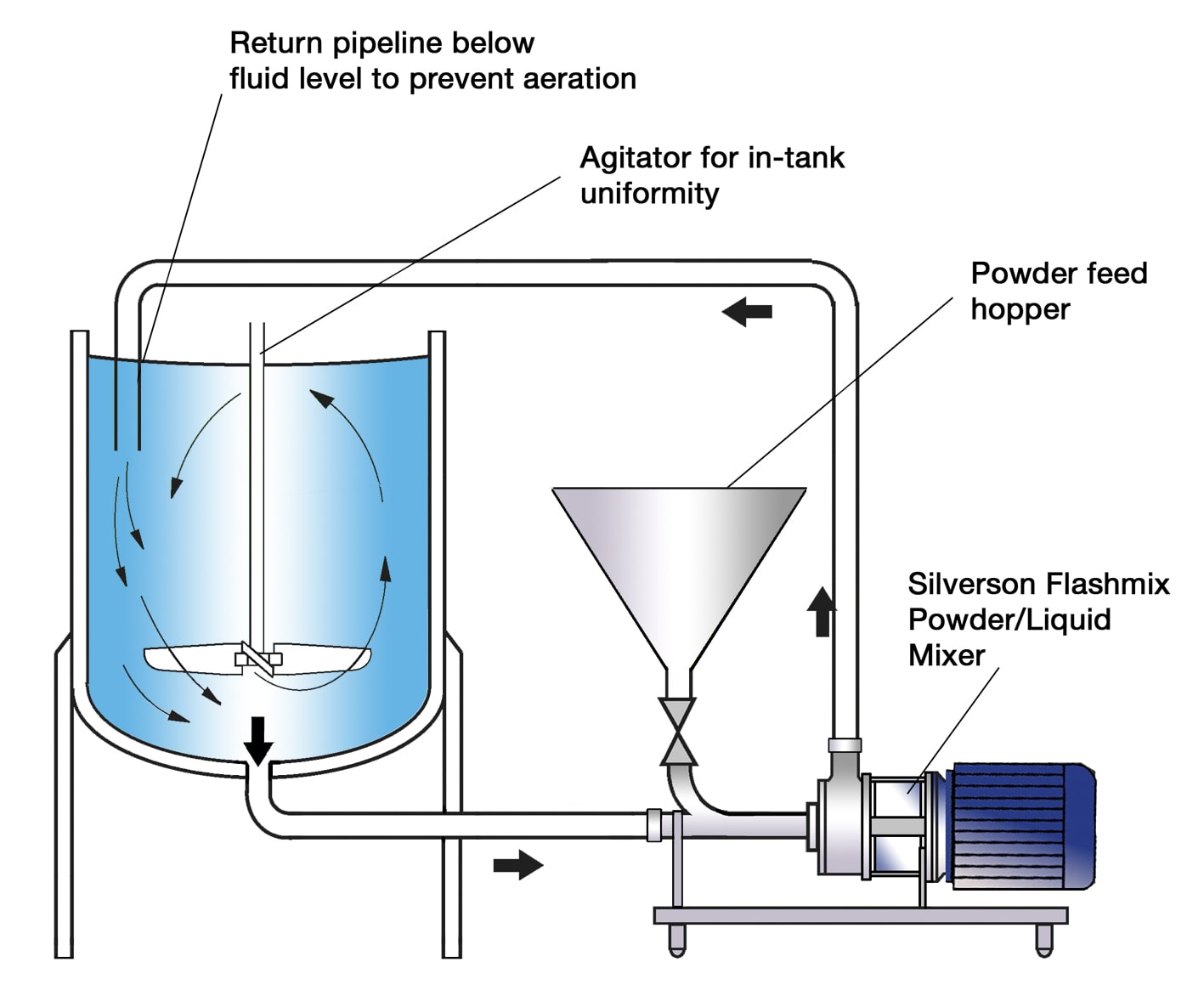
Silverson Flashmix
- Ideal for larger batches
- Capable of rapidly incorporating large volumes of powders
- Minimized aeration
- Minimized cleaning requirements
- Controlled powder addition rate
- Minimum operator input required
- Suitable for higher viscosity mixes
- Suitable for operation at higher temperatures
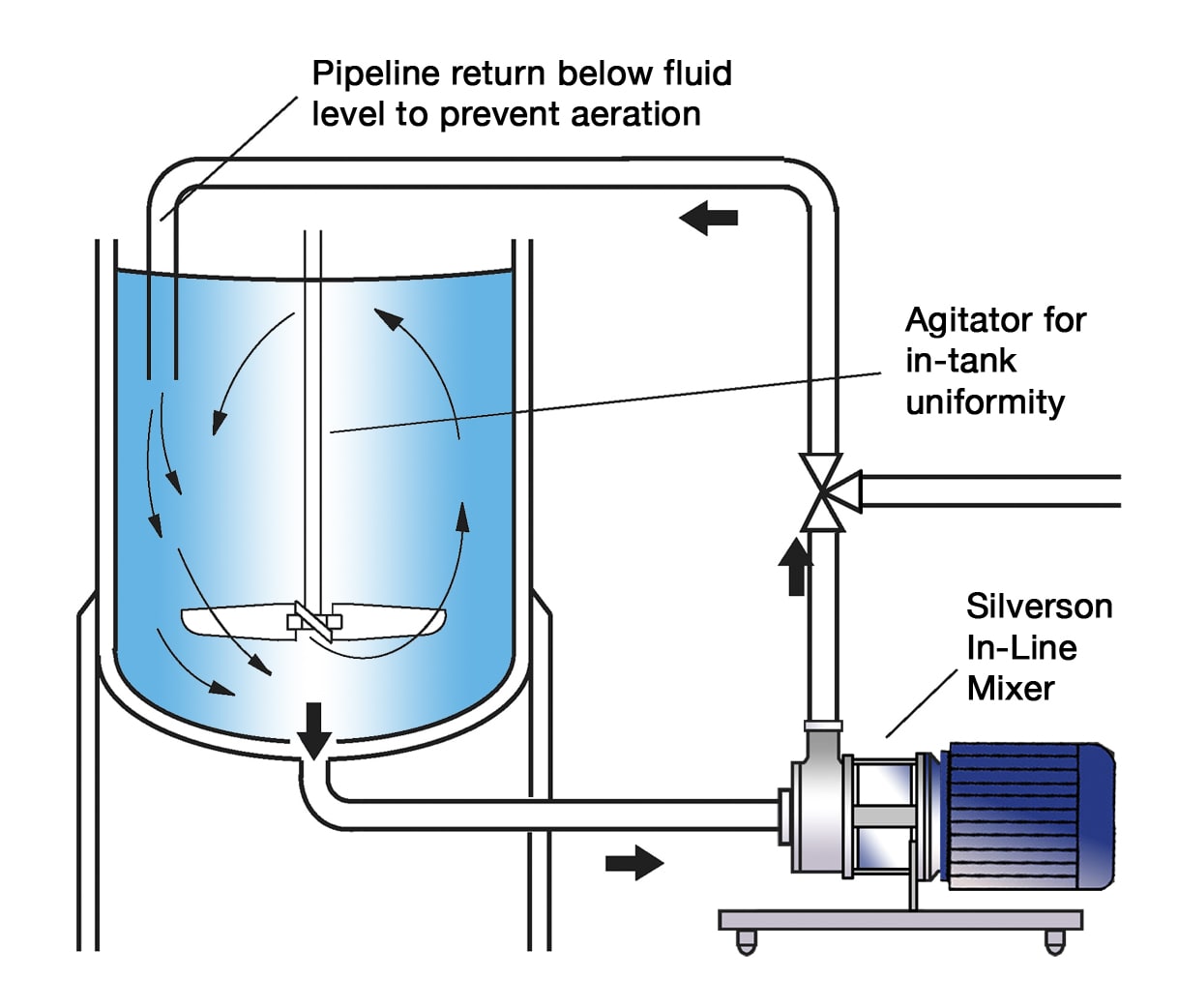
High Shear In-Line Mixers
- Ideal for larger batches
- Easily retrofitted to existing plant
- Must be used in conjunction with an efficient in-tank agitator to wet out powder
- Aeration free
- Self-pumping
- Can be used to discharge vessel
- Ultra Sanitary models available
- High Viscosity models available
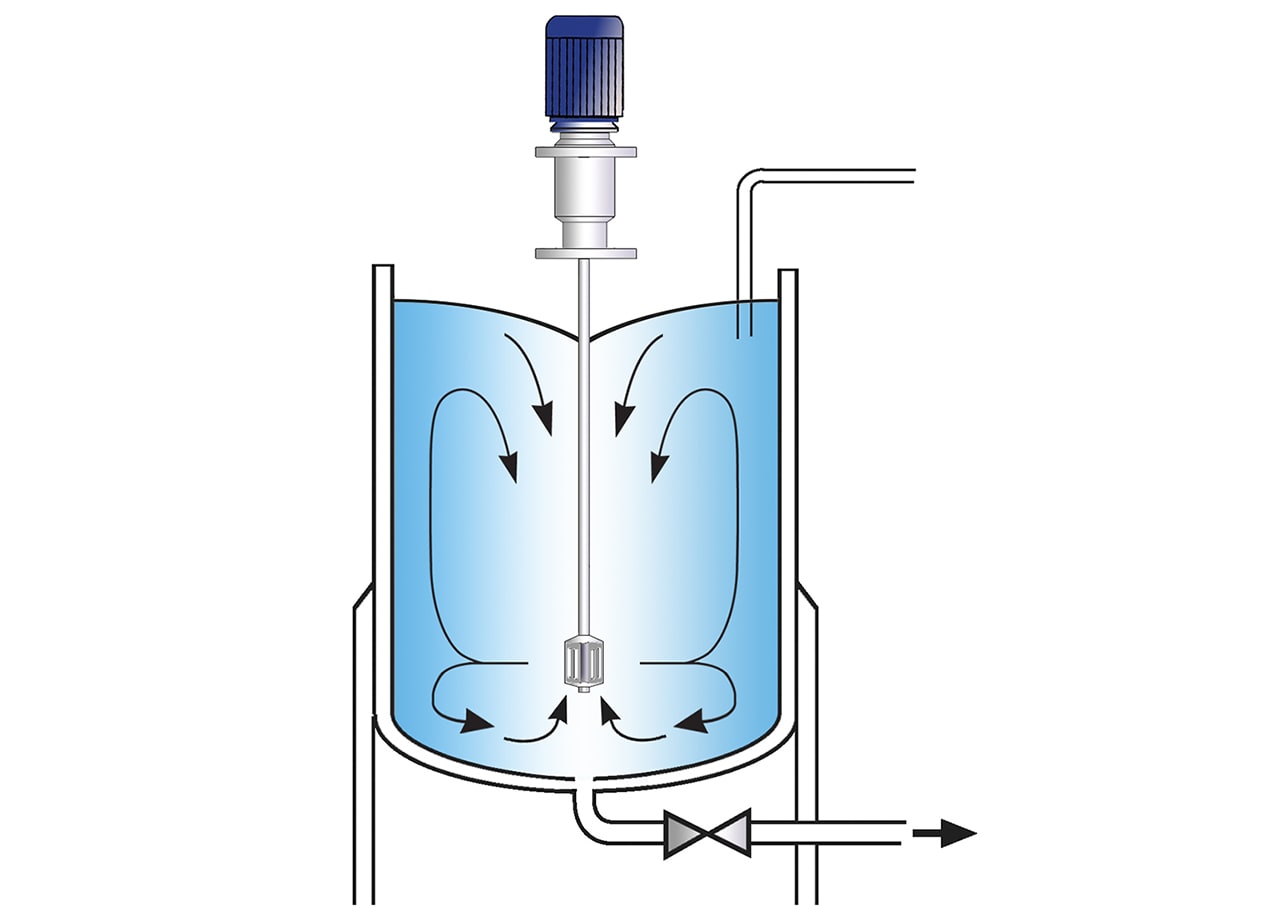
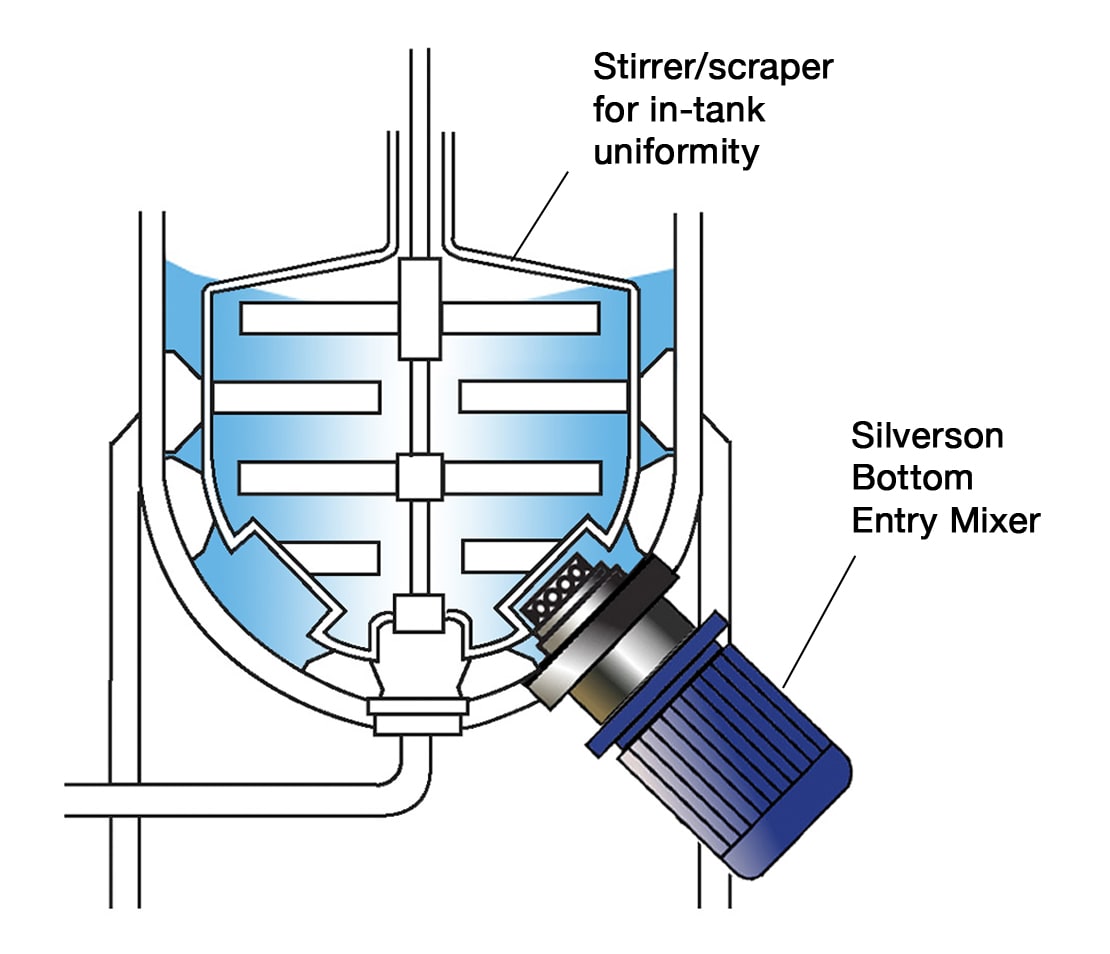
High Shear Bottom Entry Mixers
- Suitable for use on high viscosity products in conjunction with an anchor stirrer/scraper
- No immersed shaft - reduces cleaning requirements