High Speed Preparation of Rubber Solutions
Rubber solutions are used in a wide range of applications, including adhesives, sealants, paints, carpet backing compounds, tire compounds, etc. In addition to natural rubber, synthetic rubbers such as Neoprene and butadiene are also used for these applications.

The Process
The manufacturing process, product viscosity and ingredients used vary according to the end use of the rubber solution, however, a typical batch would traditionally be prepared as follows:
- The process vessel is charged with the solvent. Many types of solvent are used, including acetone, toluene, MEK, hexane, etc.
- Rubber can be supplied in either powder, crumb or block form. Blocks and large crumbs normally require chopping or granulating before they can be added to the solvent.
- The mixer is then started. Mixing continues for several hours until the rubber is fully solubilized.
- Finally, other ingredients such as pigments, fillers, stabilizers and lubricants are added and dispersed into the mix.
The Problem
Several problems can be encountered when using conventional agitators to solubilize the rubber:
- Long mixing times are required to complete solubilization.
- Chopping or grinding of rubber adds to operating costs and process time.
- Pre-crumbed/powdered rubber is expensive as the cost of crumbing is passed on to the user.
- Solvent loss must be minimized.
- Synthetic rubbers such as Neoprene are extremely tough and require a certain degree of shear to disintegrate and solubilize them.
- The solids must be prevented from sinking to the base of the vessel, as they will rapidly form a large agglomerated mass. This is virtually impossible to re-incorporate into the mix and extremely difficult to remove when cleaning the vessel.
The Solution
These problems can be overcome by using a Silverson High Shear mixer. Silverson manufactures a range of equipment for this application, from In-Line units for addition to existing process, to complete solubilization plants. Operation is as follows:
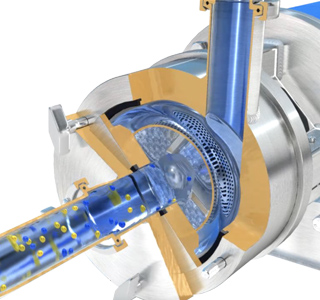
Stage 1
The powerful suction created by the In-Line mixer draws the rubber and solvent from the vessel into the rotor/stator workhead.
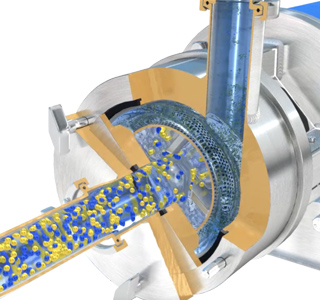
Stage 2
Centrifugal force drives the materials to the periphery of the workhead, where the rubber is subjected to a milling action in the gap between the rotor and stator.
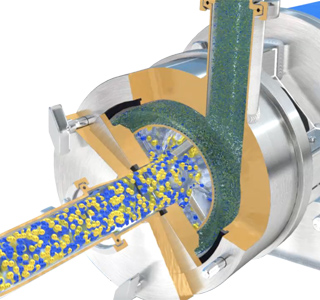
Stage 3
The product is forced out through the stator as fresh materials are drawn into the workhead. In a short mixing cycle the entire contents of the vessel passes through the workhead and solubilization is rapidly completed.
-
Stage 1

Stage 1
The powerful suction created by the In-Line mixer draws the rubber and solvent from the vessel into the rotor/stator workhead.
-
Stage 2

Stage 2
Centrifugal force drives the materials to the periphery of the workhead, where the rubber is subjected to a milling action in the gap between the rotor and stator.
-
Stage 3

Stage 3
The product is forced out through the stator as fresh materials are drawn into the workhead. In a short mixing cycle the entire contents of the vessel passes through the workhead and solubilization is rapidly completed.
The Advantages
Each of the options illustrated is preferably installed in a closed vessel, jacketed to prevent excessive temperature rise. The lid is cooled separately, causing solvent vapor to be condensed and returned to the mix. By this method there is a negligible loss of solvent without the additional expense of sealing the vessel and mixer shaft.
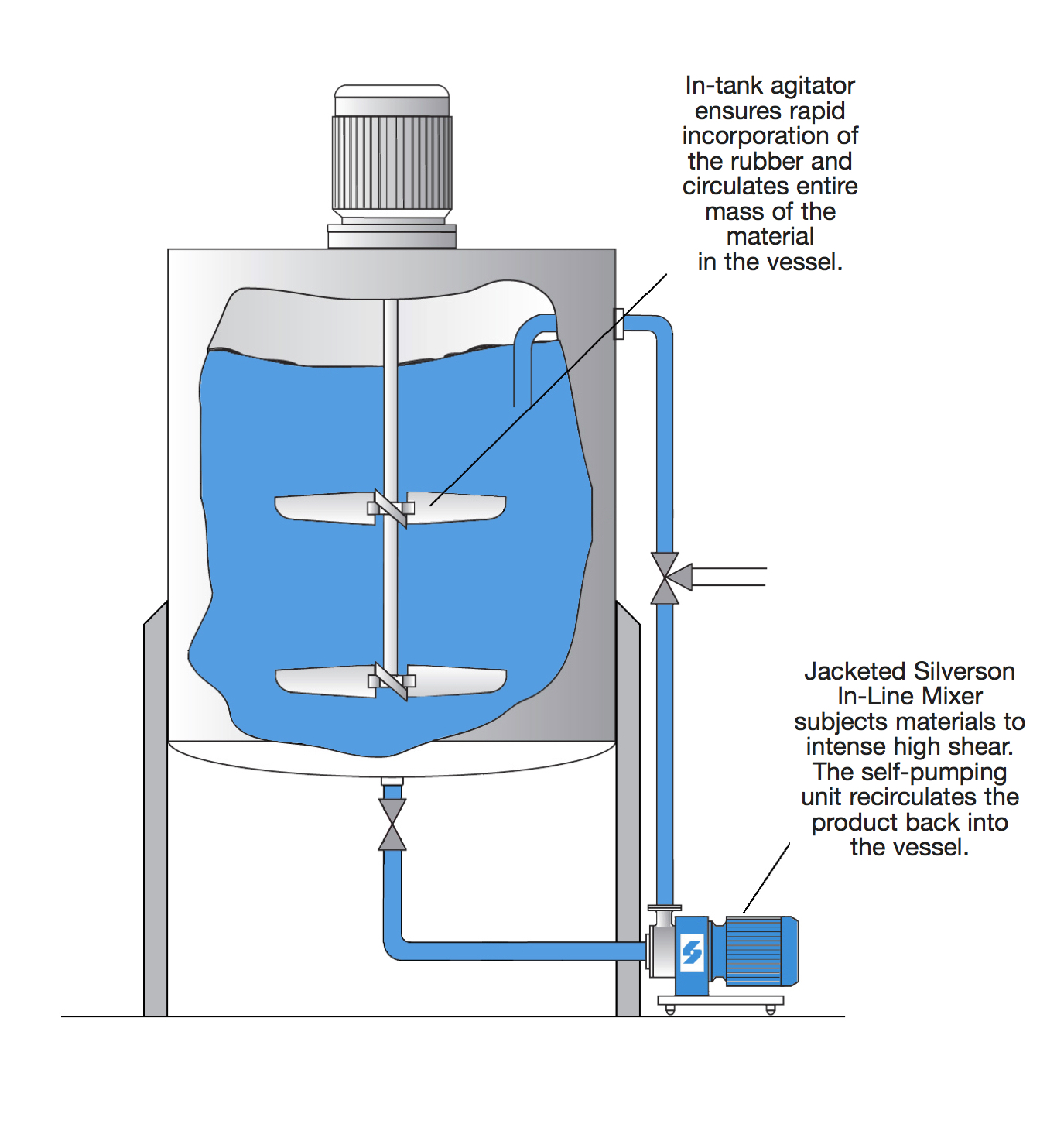
High Shear In-Line Mixer
- Must be used in conjunction with an efficient agitator as shown.
- Rubber, typically in crumb, pellet or powder form is dispersed into the solvent by the agitator.
- The materials are drawn into the In-Line mixer's workhead and subjected to intense high shear.
- Particle size is progressively reduced, exposing an increasing surface area to the solvent, accelerating the solubilization process.
- The product is recirculated back to the vessel by the self-pumping In-Line mixer.
In-Line Mixer Advantages
- In-Line mixers are easily fitted to existing plant.
- Bypassing is impossible once product is in the circulating line.
- The In-Line mixer concentrates its effort on a relatively small volume within the workhead rather than the entire batch, a more energy-efficient process.
- High rotor tip speed reduces process time.
- No additional pumping is required to circulate the product back into the tank.
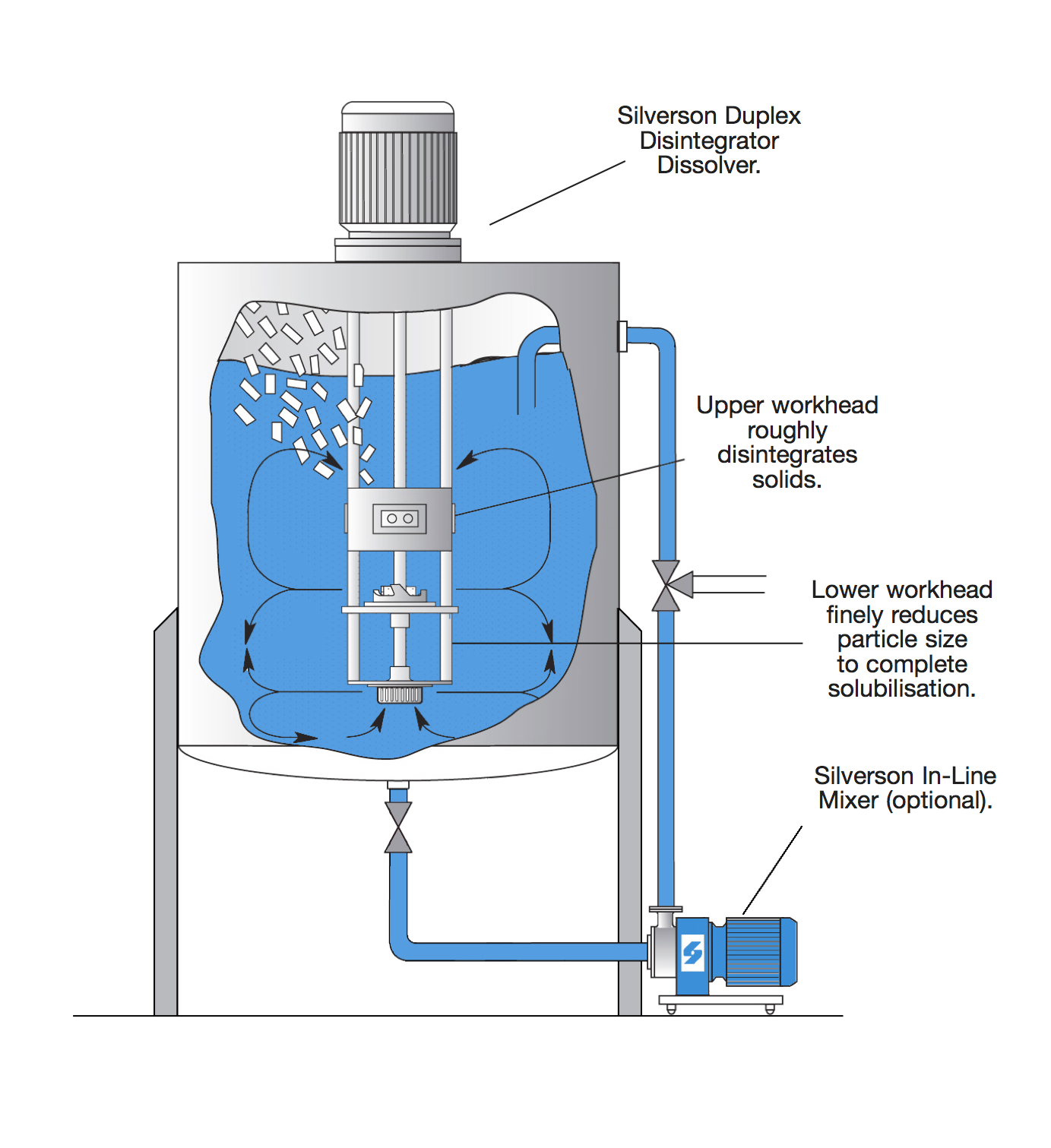
Duplex Disintegrator/Dissolver
- For processing larger crumb and small blocks, the Duplex Disintegrator Dissolver can be used in place of conventional in-tank agitation.
- The upper workhead pulls materials down from the surface of the mix and subjects them to an initial disintegration before expelling them radially back into the mix.
- The lower workhead then draws the liquid and solids upwards from the base of the vessel and further reduces the particle size, accelerating the solubilization process.
- To further reduce particle size and accelerate the dissolving process, a high shear In-Line mixer can be added to the system as shown.
Duplex Advantages
- Shredding or granulating of rubber to a fine particle size is not required. Coarsely chopped material can be added to the vessel and finely disintegrated and solubilized by the Duplex mixer. This greatly reduces overall processing time.
- Vigorous in-tank agitation ensures particles do not re-agglomerate.
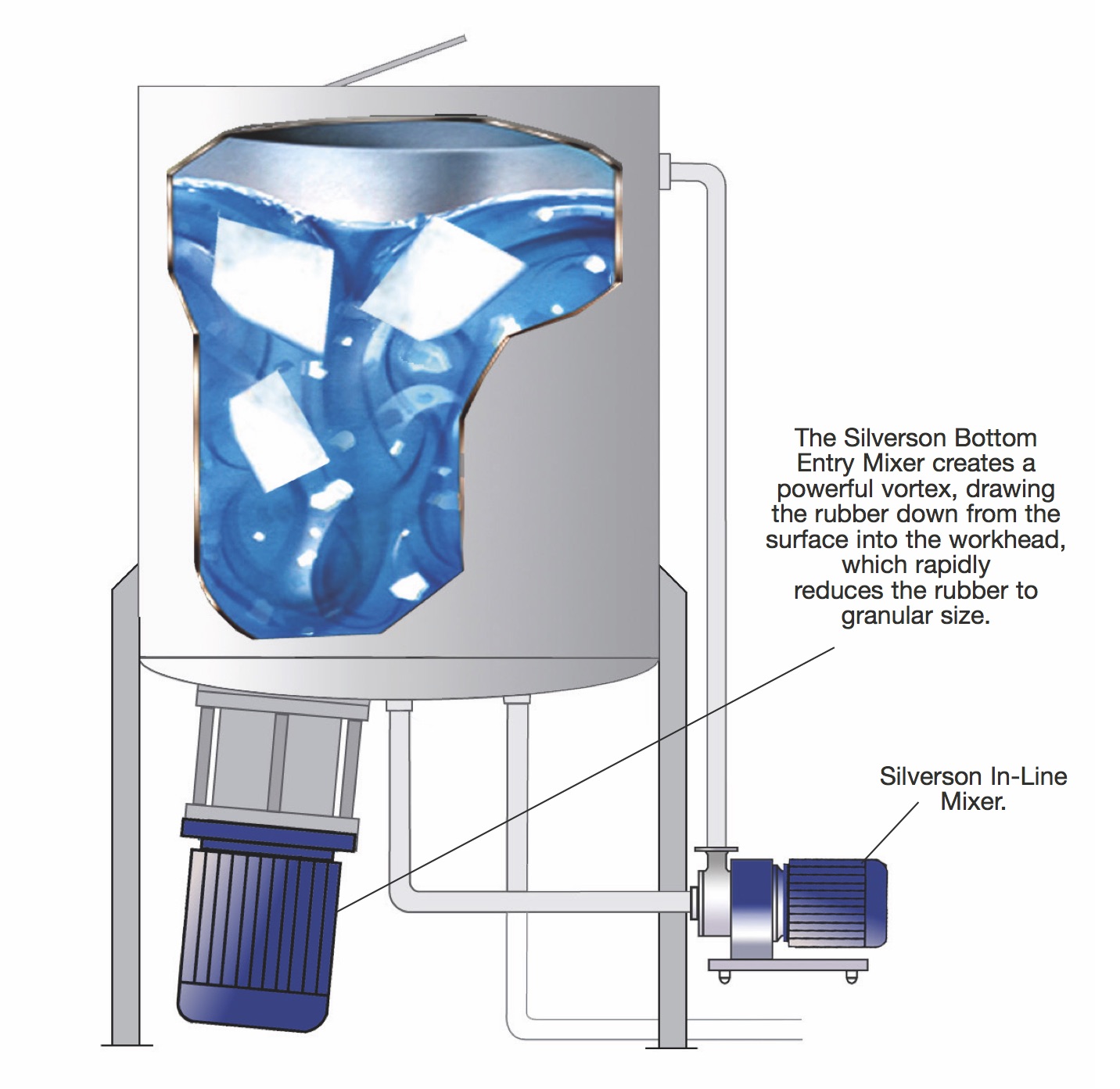
D2500 Disintegrator/Dissolver
- Rubber bales, blocks or pieces of any shape and size are added straight into the vessel.
- The rubber is drawn down from the surface into the coarse tooth disintegrating head of the Bottom Entry mixer which rapidly shreds the bales.
- When the rubber has been reduced to granular size the In-Line mixer is started, further reducing particle size.
- The combination of vigorous mixing and particle size reduction accelerates the solubilization process.
D2500 Advantages
- Rubber bales, blocks or pieces of any shape and size, even the largest commercially available, can be added straight into the vessel.
- Pre-grinding, shredding or chopping of rubber is eliminated.
- Dramatically reduced processing times.
- Easier cleaning between batches and cleaner working conditions.
- The entire operation is carried out in a single vessel.